Attenuation
Definition: Attenuation of light refers to the reduction in the intensity of light as it travels through a medium. This loss is due to a number of factors. The light:1 . spreads out and suffers an inverse square law type reduction in intensity with distance
2 .is scattered away from its original direction, or
3 . is absorbed in the medium.
In fNIRS, attenuation A in the tissue is expressed as
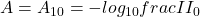 where I is the transmitted intensity and
where I is the transmitted intensity and 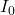 I0 the input light intensity.
I0 the input light intensity. 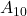 A10 is sometimes termed optical density (OD).
Depending on the context, attenuation can also be defined via the natural logarithm of the ratio of intensities:
A10 is sometimes termed optical density (OD).
Depending on the context, attenuation can also be defined via the natural logarithm of the ratio of intensities:
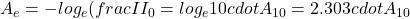 According to the modified Beer-Lambert Law, changes in attenuation are related to changes in the absorption coefficient
According to the modified Beer-Lambert Law, changes in attenuation are related to changes in the absorption coefficient 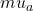 µa of the tissue
µa of the tissue
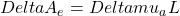
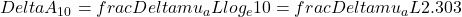 where L is the mean pathlength. On the other hand, the contributions of oxy- (
where L is the mean pathlength. On the other hand, the contributions of oxy- (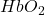 ) and deoxyhemoglobin (
) and deoxyhemoglobin (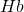 ) to the (wavelength-dependent) attenuation change are
) to the (wavelength-dependent) attenuation change are
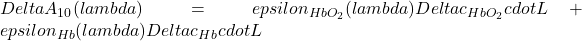 Based on measurements of
Based on measurements of 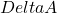 at two or more wavelengths, the resultant system of equations can be solved for the concentration changes of oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin. Note that the oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin absorption spectra in literature are usually provided in terms of
at two or more wavelengths, the resultant system of equations can be solved for the concentration changes of oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin. Note that the oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin absorption spectra in literature are usually provided in terms of 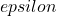 , the molar decadic absorption coefficient (unit: L mol
, the molar decadic absorption coefficient (unit: L mol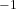 -1 cm
-1 cm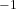 -1 or M
-1 or M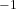 -1 cm
-1 cm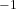 -1).
Alternative definition:
Synonym:
References: J.A. Pope. Medical Physics: Imaging. Heinemann advanced science. Pearson Education, 1999.
https://archive.org/details/medicalphysicsim0000pope
http://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008
https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.A00028
Related terms: Absorption, Scattering, Extinction, Optical Density, Modified Beer-Lambert Law
-1).
Alternative definition:
Synonym:
References: J.A. Pope. Medical Physics: Imaging. Heinemann advanced science. Pearson Education, 1999.
https://archive.org/details/medicalphysicsim0000pope
http://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008
https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.A00028
Related terms: Absorption, Scattering, Extinction, Optical Density, Modified Beer-Lambert Law
