Tissue oxygen saturation
Definition: This term refers to the saturation, or fraction of hemoglobin (expressed in %) bound to oxygen, in the microvasculature of the tissue. It is calculated from NIRS measured absolute deoxyhemoglobin and absolute oxyhemoglobin concentrations as oxyhemoglobin/total hemoglobin. It represents an average of saturation values ( in microvessels within the volume sampled by the measurement which are small enough for light to pass through. This includes arterioles, veins and venules, probably in the range of 100-200 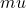 M. Very large vessels will be thick enough such that all the photons will be absorbed and no signal will be detected from them. The abbreviation was introduced because it matches the accepted format for describing oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in arteries (
M. Very large vessels will be thick enough such that all the photons will be absorbed and no signal will be detected from them. The abbreviation was introduced because it matches the accepted format for describing oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in arteries (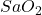 ) and veins (
) and veins (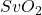 ). The term “t” for tissue was introduced because the data are from a range of vessel types within the microvasculature of the tissue.
Alternative definition:
Synonym: tissue oxygenation, tissue hemoglobin oxygen saturation
References: http://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/46/1/304
https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.412088
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0741-5214(03)01032-2
Related terms:
). The term “t” for tissue was introduced because the data are from a range of vessel types within the microvasculature of the tissue.
Alternative definition:
Synonym: tissue oxygenation, tissue hemoglobin oxygen saturation
References: http://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/46/1/304
https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.412088
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0741-5214(03)01032-2
Related terms:
