Modified Beer Lambert Law
Definition: A common approach to measuring changes in the tissue absorption using continuous waves methods is based on a generalization of Beer-Lambert law in conjunction with the assumption that the scattering properties of tissue do not vary with time. The modified Beer-Lambert law (mBLL) can be expressed as follows:
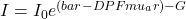 Where:
Where:
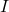 is the detected optical intensity.
is the detected optical intensity.
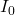
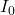 is the incident intensity.
is the incident intensity.
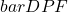 is an average (over the absorption range 0-
is an average (over the absorption range 0- 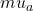 ) mean pathlength factor that depends on the optical properties of tissue
) mean pathlength factor that depends on the optical properties of tissue 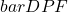 accounts for the dependence of the mean optical pathlength on scattering and absorption.
accounts for the dependence of the mean optical pathlength on scattering and absorption.
 is the inter-optode distance.
is the inter-optode distance.
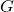 is a factor that accounts for the effect of scattering.
is a factor that accounts for the effect of scattering.
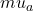
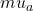 is the absorption coefficient.
By calculating logarithmic ratio of I and
is the absorption coefficient.
By calculating logarithmic ratio of I and 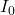 , we estimate the attenuation OD (optical density):
, we estimate the attenuation OD (optical density):
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com A = OD = log_{10}frac{I_0}{I} = frac{[bar{DPF} mu_a r + G]}{log_e(10)}](http://latamnirs.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f6c2972c6eedf1a9b75e5d0373df849b_l3.png) which is the integral form of the mBLL. It is valid for an arbitrary medium in terms of its geometry and spatial distribution of the scattering coefficient.
If we assume that G is constant and that the absorption change in the medium between a baseline condition and a test condition is small compared to
which is the integral form of the mBLL. It is valid for an arbitrary medium in terms of its geometry and spatial distribution of the scattering coefficient.
If we assume that G is constant and that the absorption change in the medium between a baseline condition and a test condition is small compared to 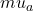 , it can be shown that the logarithmic difference between the detected intensity at baseline and during the test condition can be written as follows:
, it can be shown that the logarithmic difference between the detected intensity at baseline and during the test condition can be written as follows:
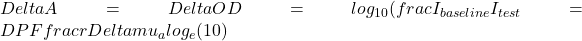 where:
Differential pathlength factor (DPF) is defined as the ratio of the mean pathlength of detected photons at baseline to the inter-optode distance. The last equation is the differential form of the mBLL and it is valid for an arbitrary medium in terms of its geometry and spatial distribution of the optical properties at baseline. The only requirement is that
where:
Differential pathlength factor (DPF) is defined as the ratio of the mean pathlength of detected photons at baseline to the inter-optode distance. The last equation is the differential form of the mBLL and it is valid for an arbitrary medium in terms of its geometry and spatial distribution of the optical properties at baseline. The only requirement is that 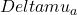 is spatially uniform.
The change in the absorption coefficient
is spatially uniform.
The change in the absorption coefficient 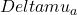 is the summation of the changes in the absorption contributions associated with available chromophores in the medium e.g O
is the summation of the changes in the absorption contributions associated with available chromophores in the medium e.g O Hb and Hb which are given by the product of their molar decadic absorption coefficients (
Hb and Hb which are given by the product of their molar decadic absorption coefficients ( 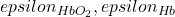 and their concentration changes:
and their concentration changes:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com Delta mu_a (lambda) = log _e(10) cdot [ epsilon_{HbO_2}(lambda) Delta c_{HbO_2} + epsilon_{Hb}(lambda) Delta c_{Hb} ]](http://latamnirs.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6fe31c412484763a84677cccd177f9af_l3.png) The change in absorbance can then be written for two wavelengths (
The change in absorbance can then be written for two wavelengths (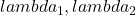 ) and two chromophores (O
) and two chromophores (O Hb, Hb) as below, assuming DPF to be independent of wavelength:
Hb, Hb) as below, assuming DPF to be independent of wavelength:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com Delta A(lambda_1) = DPF cdot r cdot [ epsilon_{HbO_2}(lambda_1) Delta c_{HbO_2} + epsilon_{Hb}(lambda_1) Delta c_{Hb} ]](http://latamnirs.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-62d8161ef0de0a374d79cce62f0f7c05_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com Delta A(lambda_2) = DPF cdot r cdot [ epsilon_{HbO_2}(lambda_2) Delta c_{HbO_2} + epsilon_{Hb}(lambda_2) Delta c_{Hb} ]](http://latamnirs.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f1f7413462779c8887ca47cb6179fb63_l3.png) One can estimate the concentration changes of both hemoglobin species by solving this system of linear equations.
Alternative definition:
Synonym: modified Bouguer-Beer-Lambert Law
References: https://doi.org/10.1039/9781847551207
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/5/N02
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/49/14/N07
Related terms: Beer Lambert Law, Light Intensity, Molar Absorption
One can estimate the concentration changes of both hemoglobin species by solving this system of linear equations.
Alternative definition:
Synonym: modified Bouguer-Beer-Lambert Law
References: https://doi.org/10.1039/9781847551207
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/5/N02
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008
https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/49/14/N07
Related terms: Beer Lambert Law, Light Intensity, Molar Absorption
